VOLUME FLOW AND NEGATIVE PRESSURE - WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN DUST EXTRACTORS AND INDUSTRIAL VACUUM CLEANERS?
A dust extractor removes airborne dust particles and fumes, whilst an industrial vacuum cleaner absorbs settled dust particles and coarser impurities. To fulfil these different purposes, among other things, the volume flow and negative pressure are used in the devices in opposite ways.


To generate clean air, a dust extractor requires a large volume flow and a low negative pressure. In order to be able to extract dust from surfaces, an industrial vacuum cleaner, on the other hand, requires a high negative pressure, but a low volume flow. The following comparison between an ESTA dust extractor and an ESTA industrial vacuum cleaner, each with 2.2 kW drive power, illustrates how these are used in opposite ways:
| Comparison | Dust extractor (DUSTOMAT 4-10) | Industrial vacuum cleaner (EUROSOG I-D) |
|---|---|---|
| Max. negative pressure [Pa] | 2,600 | 19,500 |
| Max. volume flow [m³/h] | 2,000 | 360 |
| Connection-Ø [mm] | 160 | 50 |
For a better understanding of this principle, the terms "volume flow" and "negative pressure" are defined in greater detail below.
WHAT IS A VOLUME FLOW?
A volume flow is the volume of a medium (gas or liquid) that moves through a defined cross-section (e. g. a pipe) in a certain time. For this movement to take place at all, there must always be a pressure difference between at least two spaces / volumes (see "What is negative pressure?"). With reference to an extraction system, the volume flow describes how much air flows through an extraction pipe in a given time. Even in everyday life we encounter the volume flow, for example in the tap, in rivers and streams, but also in gaseous form in the air, in air conditioning systems and fans.
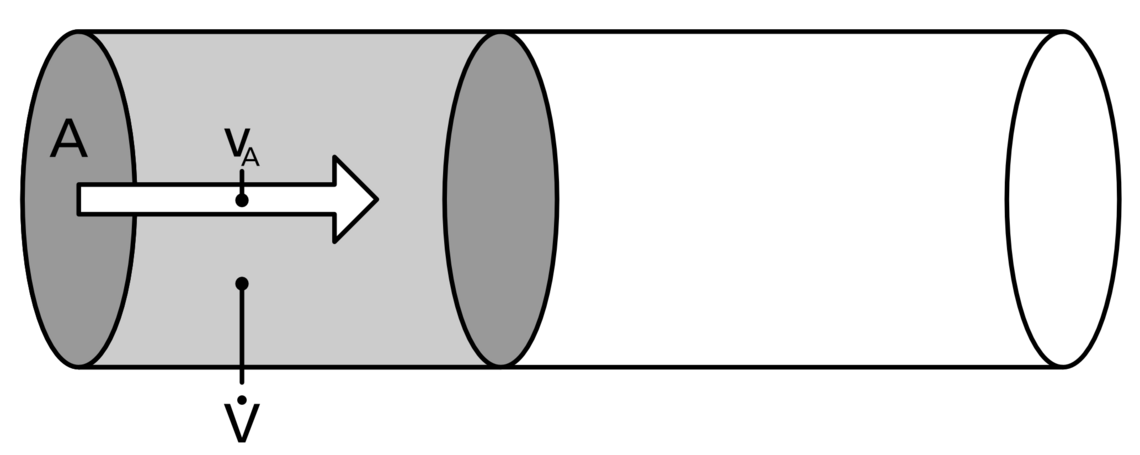
The usual unit of a volume flow is m³ / h. A volume flow is calculated using the following formula:

With an air volume flow of 2,000 m³ / h, 2,000 cubic metres of air per hour thus flow through the defined cross-section of a pipe. The optimal air volume flow of an extraction system depends on the application.
WHAT IS NEGATIVE PRESSURE?
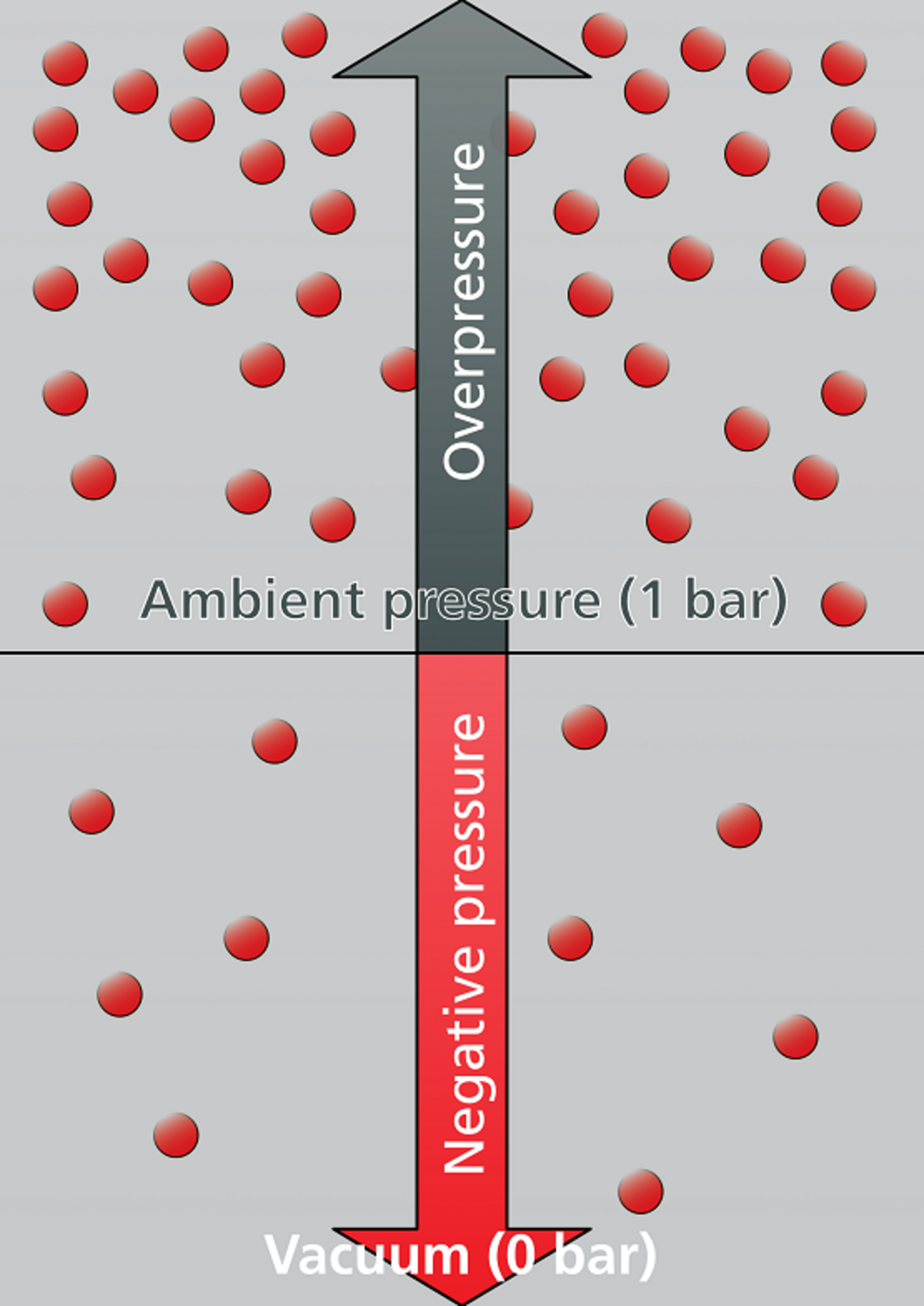
The term negative pressure refers to the pressure in a defined volume, provided that it is below the ambient pressure.
The use of the term negative pressure is only appropriate if a reference pressure is present. The reference pressure used in the current standards is the value of one bar (1 bar). The former measure of negative pressure was given in atmospheres (atm); bar has been used since 1978. Since the value of the vacuum is below the reference pressure, it is also called negative pressure.
For example, if you suck in air with a fan, it creates air suction that can cause negative pressure. However, the further flow of air in the unlimited space almost compensates for this effect. If there is a spatial limitation, though (e. g. through a pipe), a defined negative pressure builds up as a function of the volume flow and the pipe diameter. The operating principle of a vacuum cleaner is based on this type of generation of negative pressure. In the housing of a vacuum cleaner there is a blower that pulls the air through the vacuum cleaner tube and blows it out again at the other end. The resulting negative pressure ensures that the ambient air and thus the dirt particles are sucked into the vacuum cleaner. The negative pressure increases with the same cross-sectional area and a stronger blower. Exactly the same applies with decreasing cross-sectional area and the same blower output.
As a result, it can be seen that an industrial vacuum cleaner uses a high negative pressure to generate a force great enough to suck up larger settled particles. A large volume flow is not required for this purpose. However, as dust removal systems focus on the cleaning of larger air masses, a large volume flow is indispensable here. The fumes and suspended particles in the air are small and light particles. Thus, they can be sucked up without too much negative pressure.
A SUITABLE EXTRACTION SYSTEM
INDUSTRIAL VACUUM CLEANERS
For vacuum cleaning applications, ESTA offers mobile industrial vacuum cleaners such as the EUROSOG, DUROSOG and WHISPERSOG. The central vacuuming station CENTRASOG CVS 2.0 completes the product portfolio.
DUST EXTRACTORS
For dust extraction applications, ESTA’s range includes, for example, the DUSTOMAT 4 mobile dust extractor, the stationary dust extractor MOBEX and ESTMAC or the DUSTMAC modular stationary dust extraction system. The drive and filter performance can be graduated in all three extraction devices.
"Which extraction system with which performance level is the right one for my application?" The ESTA service team will be happy to help you with this question. Just get in touch with us.
CONTACT
WE ARE HAPPY TO PROVIDE A PERSONAL CONSULTATION
We can adapt our exhaust installations to your needs. Tailor-made, modular and individual. Ask us!

















